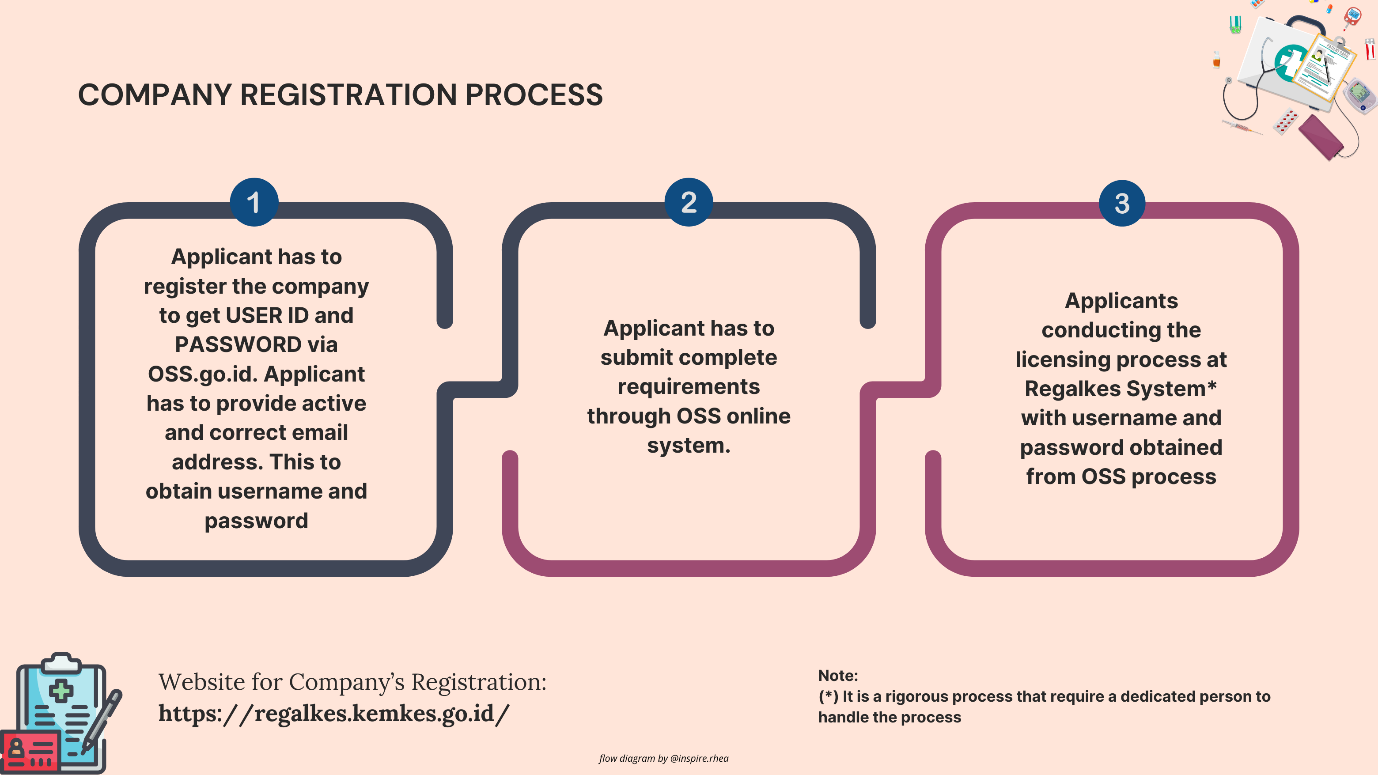
- Set Up an Account on Regalkes: Begin by creating an account on the Regalkes platform. This requires providing business details and the authorized representative’s contact information. For foreign manufacturers, it is mandatory to appoint a local distributor who holds the necessary Medical Device Distributor License (MDDL).
- Prepare and Upload Documentation: After account setup, submit all the required documents through the Regalkes platform. The documentation should be complete and accurate to avoid delays in processing. Any missing or incorrectly translated documents can lead to rejection or extended review periods.
- Pay the Registration Fee: Upon submission, the Ministry of Health generates an invoice for the application fee. Class A devices typically cost around IDR 1,500,000 (USD 125), Class B and C devices cost about IDR 3,000,000 (USD 225), and Class D devices are priced at IDR 5,000,000 (USD 350). Payments must be made within 7 calendar days of receiving the invoice.
- Review and Evaluation: The Ministry of Health will evaluate the submitted documentation, and the review period varies depending on the class of the device:
- Class A: 45 days
- Class B: 90 days
- Class C: 100 days
- Class D: 120 days
If additional information is required, the Ministry will notify the applicant and request the necessary documents. Applicants have 10-15 working days to submit the required documents for re-evaluation.
5. Issuance of Nomor Izin Edar (NIE): Once the Ministry of Health approves the registration, it will issue the Nomor Izin Edar (NIE), a regulatory license required for legally marketing the device in Indonesia. The license is valid for up to 5 years, after which a renewal process is required.
- Class D: 120 days
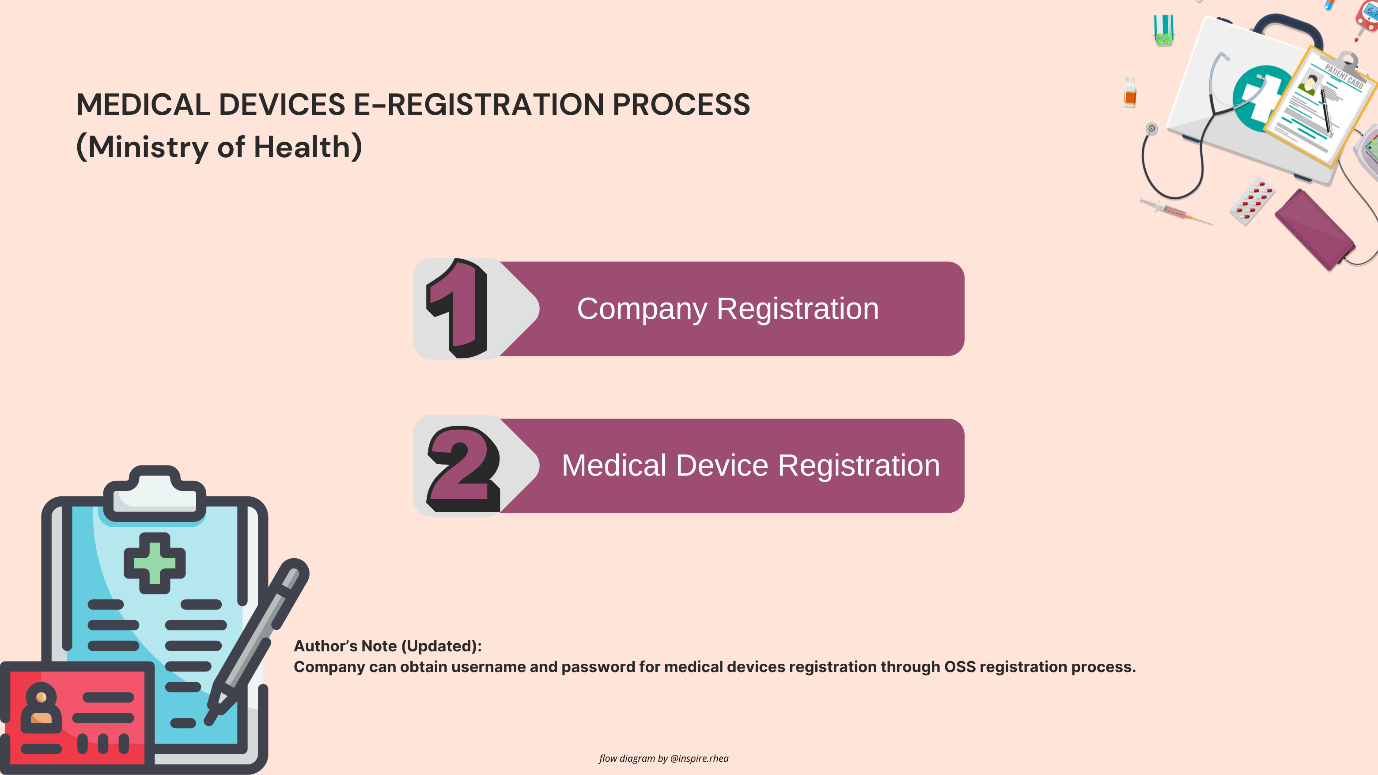
- Image 3: General Step Prior to Medical Devices Registration
4. Medical Device Certification Indonesia: Costs and Timelines
The timeline for medical device certification Indonesia can vary depending on the device class. Typically, the registration process is faster for Class A devices and slower for Class C and Class D devices due to the more rigorous testing and documentation requirements.
Here’s a quick summary of costs and timelines:
- Class A: Cost USD 125, processing time 1-2 months.
- Class B and C: Cost USD 225, processing time 3-4 months.
- Class D: Cost USD 350, processing time 4-6 months.
Additionally, device renewals typically cost IDR 1,000,000 (USD 75) and must be completed every 5 years.

5. e-Catalogue Registration: A Competitive Advantage
For businesses aiming to supply medical devices to public hospitals and healthcare institutions, e-catalogue registration Indonesia is an essential step. The e-catalogue is an online procurement system used by the Indonesian government to purchase medical products from registered manufacturers.
To register in the e-catalogue, businesses must meet specific Good Distribution Practice (GDP) requirements and provide comprehensive documentation, including the medical device’s Nomor Izin Edar (NIE). Listing in the e-catalogue offers several advantages:
- Government Access: Public hospitals and healthcare facilities use the e-catalogue to source medical devices, providing manufacturers with a direct link to these institutions.
- Market Visibility: Devices registered in the e-catalogue are prioritized for government procurement, which can significantly increase sales volume.
- Reduced Markups: When devices are listed in the e-catalogue, there is no room for regional dealer margins, improving pricing and competition.
6. Challenges in the Medical Device Registration Process
While the medical device registration Indonesia process is straightforward, there are some common challenges that businesses may face:
- Language Barriers: All documents must be translated into Bahasa Indonesia, and failure to provide accurate translations can lead to delays.
- Local Testing: For Class C and D devices, some may require testing in local accredited laboratories, adding to the cost and time required for approval.
- Distributor and License Transfer Issues: Once a distributor has been selected, switching to another distributor can be challenging. The license is typically non-transferable and may require reapplication, causing significant delays.
- Complex Documentation: For higher-risk devices, such as Class D, companies must submit more comprehensive clinical data, making the documentation process complex and time-consuming.
Conclusion
Successfully navigating the medical device registration Indonesia process is key for businesses looking to enter the market. By understanding the device classification system, preparing the correct documentation, and following the necessary steps through the Regalkes platform, companies can achieve smooth market entry. Additionally, registering in the e-catalogue can further enhance access to public institutions, offering a competitive advantage in the Indonesian healthcare sector.
With thorough preparation and a clear understanding of the regulatory requirements, businesses can confidently enter the Indonesian market and bring their medical products to consumers in this rapidly growing healthcare landscape.